Projection Solver
A C++ solver to calculate projection of 3D STL geometries on a user-defined plane
While working on the project, Thermal Protection System modeling, during the second year of my Ph.D., I had written a naively parallel code that calculates the projection area of any 3-D microstructure on an intersected plane at any angle. It was partly just as an exercise to familiarize myself with C++14 and 17 syntaxes and coding using templates. Perhaps, the ablation community and those who need some computational geometry algorithms may benefit from this. Here is the Github link.
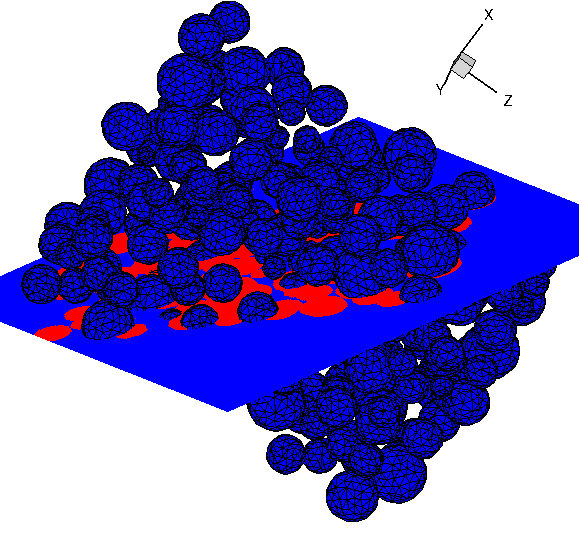
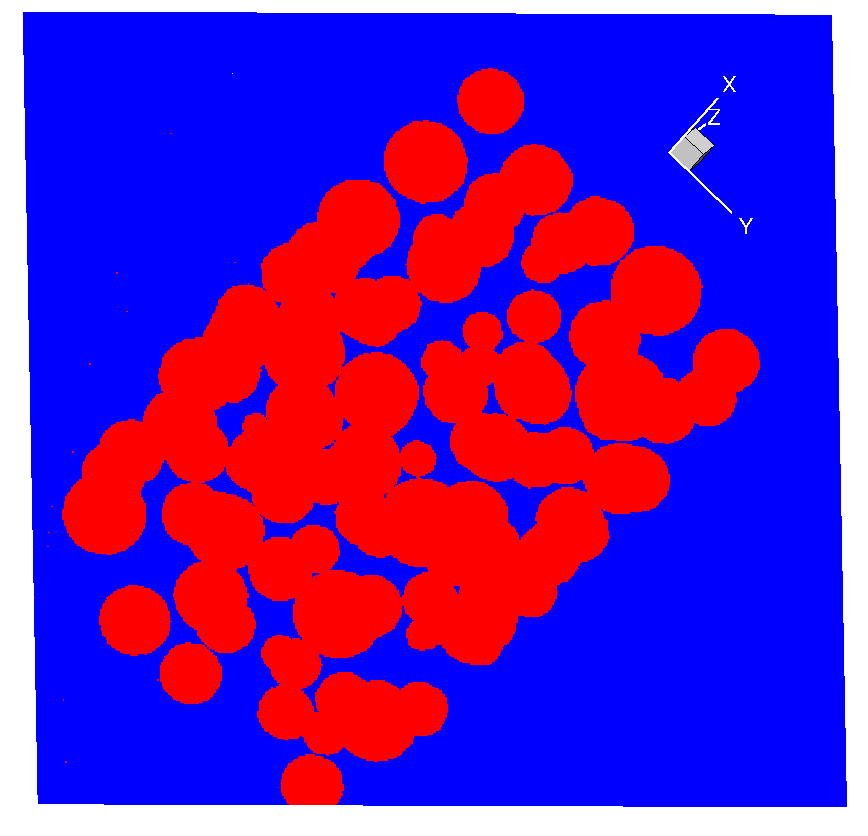
Fig. 1. (a) STL geometry representing a 3D microstructure of a heatshield intersected by a plane at some angle. The surface of the plane shows the projected image of the 3D structure on a plane, calculated using a ray-tracing algorithm. (b) Full view of the projection.
The code calculates the projection of microstructure on a plane. The STL geometry is centered at the origin. A plane is also centered at the origin and it can be aligned in (+/-) X, Y, Z directions. The plane can be rotated in 3D by specifying Euler angles alpha, beta, and gamma. First, cells lying inside the geometry are tagged (InOutFlag). Then, a ray is sent along the direction of the normal to find out the intersection of panels lying above the plane. Finally, with enough refinement of the plane, accurate area can be computed.
The code uses message passing interface (MPI) for parallel communication. The partitioning strategy is naive but serves the purpose. The images shown in the Output folder are calculated using 1,024 processors for a 512x512 grid. I cannot provide the STL geometry because it was created for my research project on ablative materials.
To group the files from multiple processors generated in Output, the python script groupPlanes.py is provided.